Background
The 5G roll-out competitions among global leaders in telecommunication have driven technological innovations in the wireless connectivity, as there have been partnerships formed between major telecom service providers and leading SD-WAN vendors, for example, Verizon and Cisco. On the other hand, SD-WAN has already been adopted as the complementing technology to existing 4G LTE links to deliver mobile business applications in satisfying performance.
To Figure Out The Best of 5G
Despite the recent hyped launches of 5G by leading telecom service providers, the real-life performance of this new generation network remains questionable. The reasons lie in the deployment efforts and management. First, large-scale organizations with multiple branches may take longer to deploy and integrate 5G cellular networks in their cloud and edges. In fact, these organizations rely heavily on mobile business applications, such as VoIP, video conferencing, cyber security, and mission-critical IoT or IIoT deployments, which largely occupy bandwidth particular for the mobile broadband. Secondly, the management of connectivity between cloud and edge, campus and branches must be taken into considerations when deploying 5G.
Therefore, in order to realize the full capability of 5G, telecommunication leaders have formed partnerships to enhance mobile SD-WAN offering. By integrating 5G cellular connectivity with SD-WAN, the digital network infrastructure is enabled with end-to-end visibility, security and application-optimized management. Packets can be routed to the optimal channels to further reinforce expectations of 5G in mobile business applications. Personnel with mobile 5G smart devices will strongly feel the reliable, steady performance.
On the other hand, SD-WAN enables the automated policy execution across campus and branch networks. Such policies include network-slicing and intent-based networking, which play critical parts in edge A.I. computing and provisioning.
Evolutions by Mobile SD-WAN
Mobile SD-WAN has contributed to the evolution of network management. Since the introduction of smart mobile devices, the network traffic has grown exponentially in a dramatic pace. In fact, the introduction of 4G LTE and the upcoming 5G have demonstrated that wireless connectivity will continue to be preferred networking deployments over the wired infrastructure. To meet the Big Data, mobile SD-WAN presents the cost-effective and agile opportunity to enhance the connectivity for distributed network architecture.
SD-WAN can be deployed on top of existing Internet, cellular networks (regardless of 4G or 5G), and also MPLS by adopting virtualized white-box server to run mobile business applications. IT personnel can automate packets of certain applications and services to pre-defined locations. This is particularly beneficial for corporations with branches worldwide, as the packets generated from branches can be automated to be routed to destined servers.
Recommended Solutions
The real potential of 5G lies in the edge, basically by the IoT/A.I gateways, which will run the compute, analytics and storage functions at the edge, to enable intent-based networking and network slicing. Suggested edge gateways include NCA-1010, V3S and V6S from Lanner Electronics Inc.
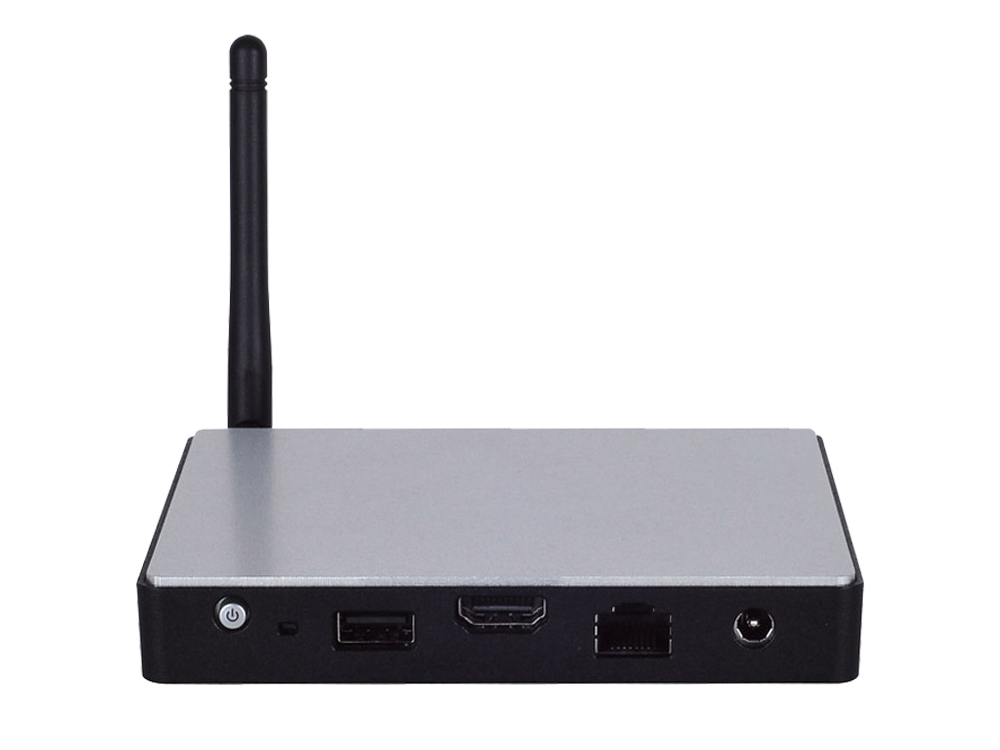
NCA-1010 is Lanner’s revolutionary ultra compact x86 networking system built with Intel® Atom™ E3815/E3825 SoC. The central processor comes with hardware-assisted security mechanisms including AES-NI, allowing only authorized software or data to run on NCA-1010. Despite its compact size, NCA-1010 delivers rich I/O connectivity and scalability, including one HDMI port, one console port for device network management, three LAN ports, two USB ports (USB 2.0/3.0), and one antenna hole for signal reception.
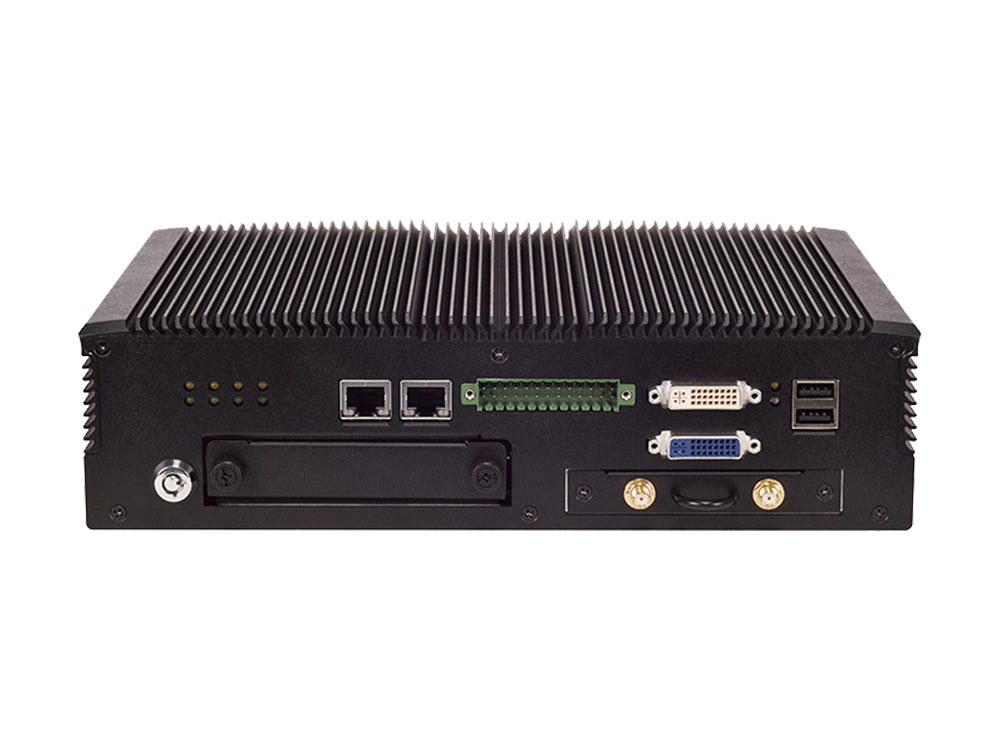
For analytics performance and ruggedness in IoT/IIoT applications, Lanner’s V3S fits the bill. The mobile edge gateway is powered by 14 nm Intel® Atom™ x7-E3950 SoC (formerly Apollo Lake). This processor consumes low volume of power and offers performance upgrade. V3Sboasts an abundance of I/O peripheral connectivity including 2 x serial COM ports, 2x video output by DVI-D, USB and Digital I/O ports, 6x RJ-45 ports (4 with PoE) and removable SATA storage bay. To enable wireless network connectivity, V3S offers 2 mini-PCIe sockets with swappable dual SIM slot supporting 3G/4G/LTE cellular communications.
V3S is compliant with E13 standard and has passed MIL-STD-810G shock and vibration resistance certifications for a mobile setting. Since temperature is a concern when deployed outdoors, V3S is built to support wide temperature range, from -40 to 70°C.
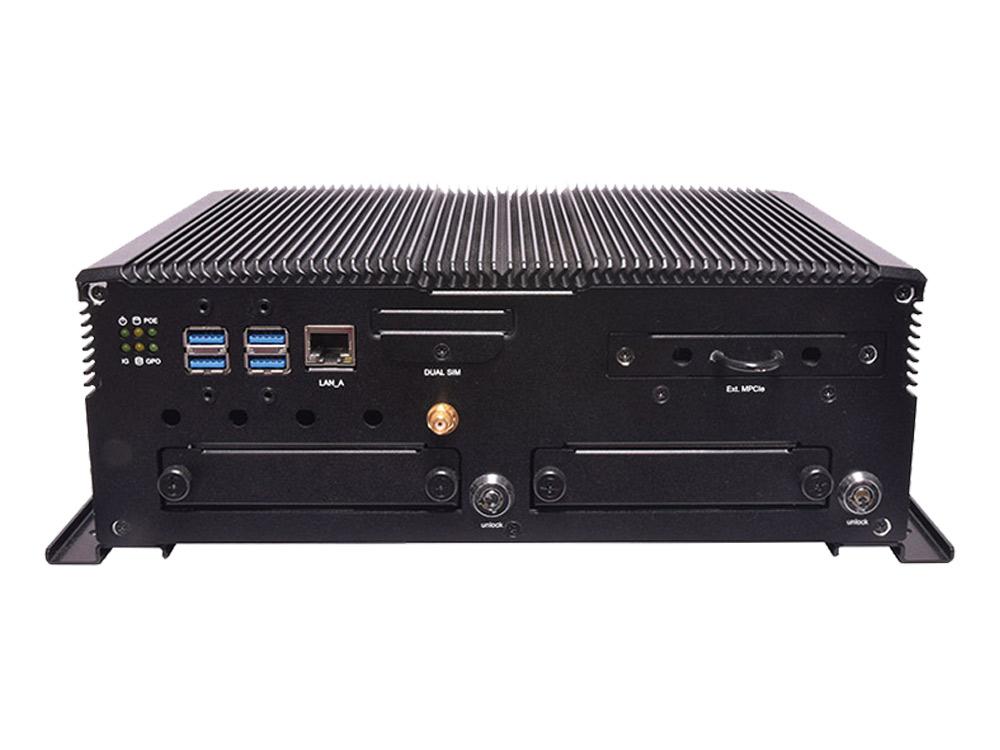
V6S can be considered as an high-end version of V3S in edge analytics. The mobile gateway is powered by the 7th Generation 14 nm Intel® Core™ i7-7600U SoC (formerly Kaby Lake), offering power-efficient performance and accelerated graphics performance to run IoT/IIoT applications. V6S series offers 1 x GbE RJ45 ports plus 10 x RJ-45 PoE ports for IP camera connection, and two removable 2.5” HDD/SSD drive bays for the storage of recorded footages. For wireless connectivity, V6S is internally built with 1 x full-sized Mini-PCIe with dual SIM card reader, 1 x full-sized Mini-PCIe for WiFi, and 1 x external Mini-PCIe 3.0 with dual SIM card readers, which allows 4G/LTE module to be removable externally.
Like V3S, the high-end V6S also supports military standard shock/vibration resistance and wide operating temperature.