In today's network environment, organizations depend heavily on the uninterrupted operation of their IT/OT systems. Network administrators play a pivotal role in remotely monitoring and managing edge devices, ensuring that critical applications run smoothly in the distributed locations. Out-of-Band Management (OOB) has emerged as a critical component in ensuring the reliability, security, and efficiency of networked systems.
Understanding Out-of-Band (OOB) Management
Out-of-band (OOB) management is a method of remotely controlling and overseeing critical IT/OT assets and network equipment using a secure protocol connection through a secondary interface that is physically separate from the primary network connection. This setup ensures that administrators retain the ability to manage and troubleshoot devices remotely, even in scenarios where the primary network is down or encountering issues. With hardware-based out-of-band management, IT administrators can access devices even if they are turned off or the operating system (OS) is down or unresponsive.
OOB Management Implementation
The implementation of out-of-band management is straightforward: console servers are placed at each location and connected to routers, servers, switches, power controllers, and storage devices. Serial console servers, also known as terminal servers, play a crucial role by establishing an alternative remediation path for critical network devices through a distinct management plane, often utilizing a 4G LTE cellular connection. This setup empowers administrators to configure, reboot, and reset devices in case the primary network faces disruptions, ensuring organizations maintain uninterrupted availability and network resilience.
Benefits of OOB Management
- Enhanced Reliability:
OOB enhances the reliability of IT infrastructure by providing an independent and secure means of access. Even if the primary network is compromised or experiencing issues, administrators can maintain control and make necessary adjustments. - Reduced Downtime:
With the ability to remotely troubleshoot and resolve issues, OOB significantly reduces downtime. This is crucial for businesses where uninterrupted service is essential. Swift resolution of problems can minimize the impact on operations and customer experience. - Improved Security:
OOB contributes to a higher level of security by offering a separate, dedicated channel for management. This isolation helps protect critical infrastructure from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats that may target the primary network.
Applications of OOB Management
- Data Centers:
OOB is extensively used in data center environments where large numbers of servers and network devices require constant monitoring and management. Remote access to critical infrastructure ensures optimal performance and quick response to issues. - Remote Offices:
Businesses with remote offices or branch locations benefit from OOB to manage and troubleshoot IT equipment without the need for on-site personnel. This is particularly relevant in scenarios where travel to the location may be impractical or time-sensitive. - Telecommunications:
OOB plays a vital role in the telecommunications industry, where network reliability is paramount. Telecom companies use OOB to remotely manage and maintain their infrastructure, ensuring continuous service availability.
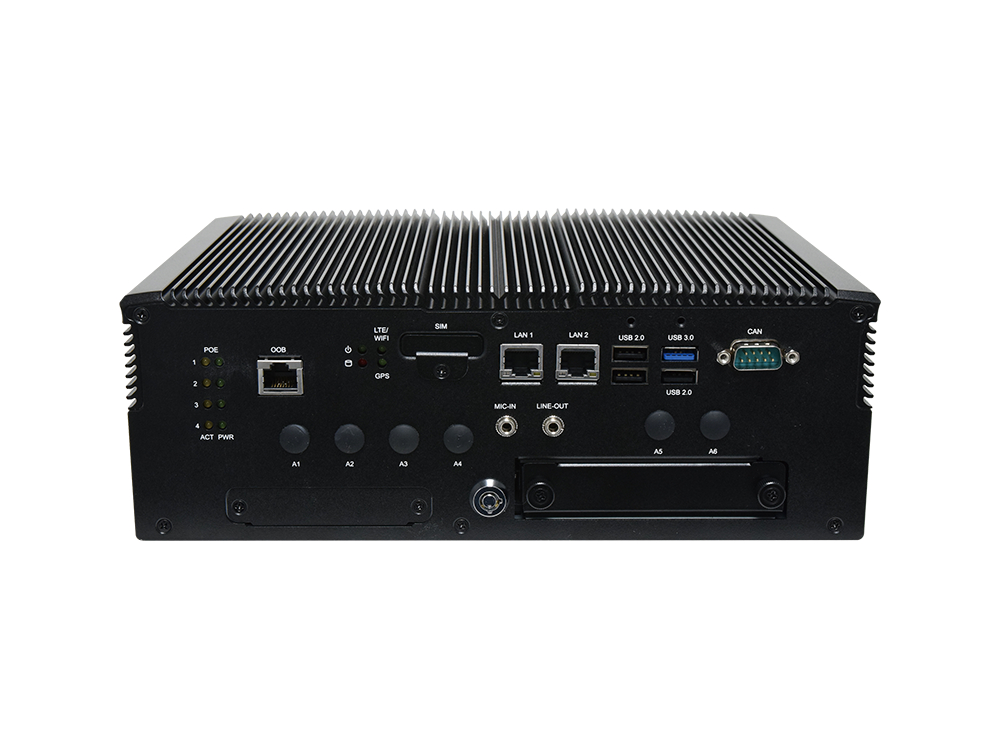
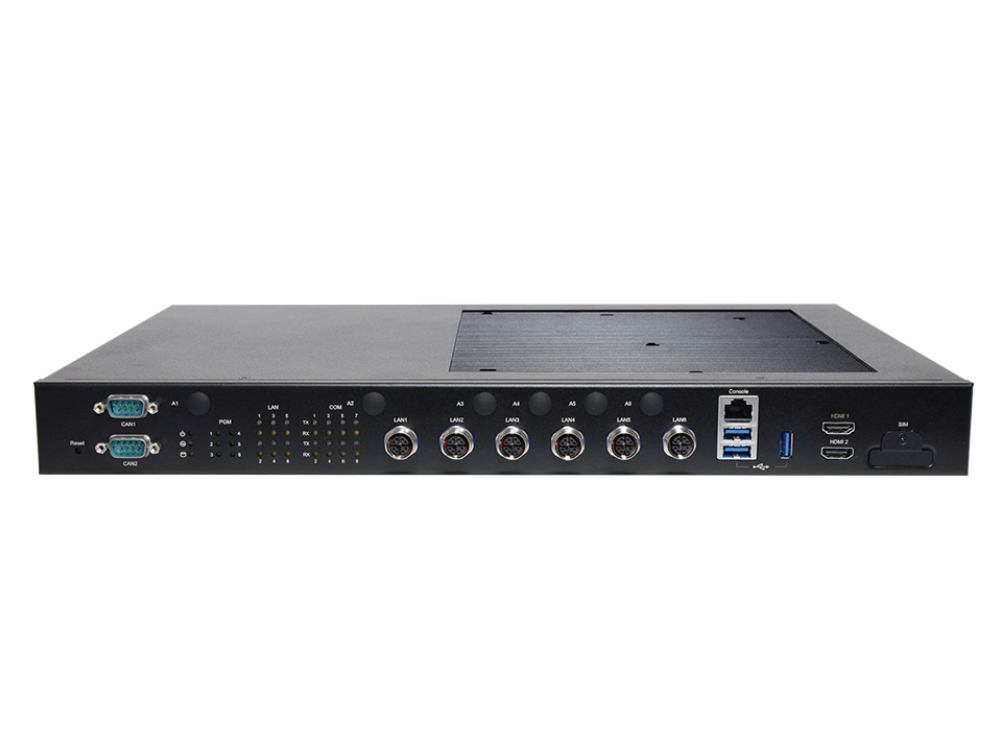
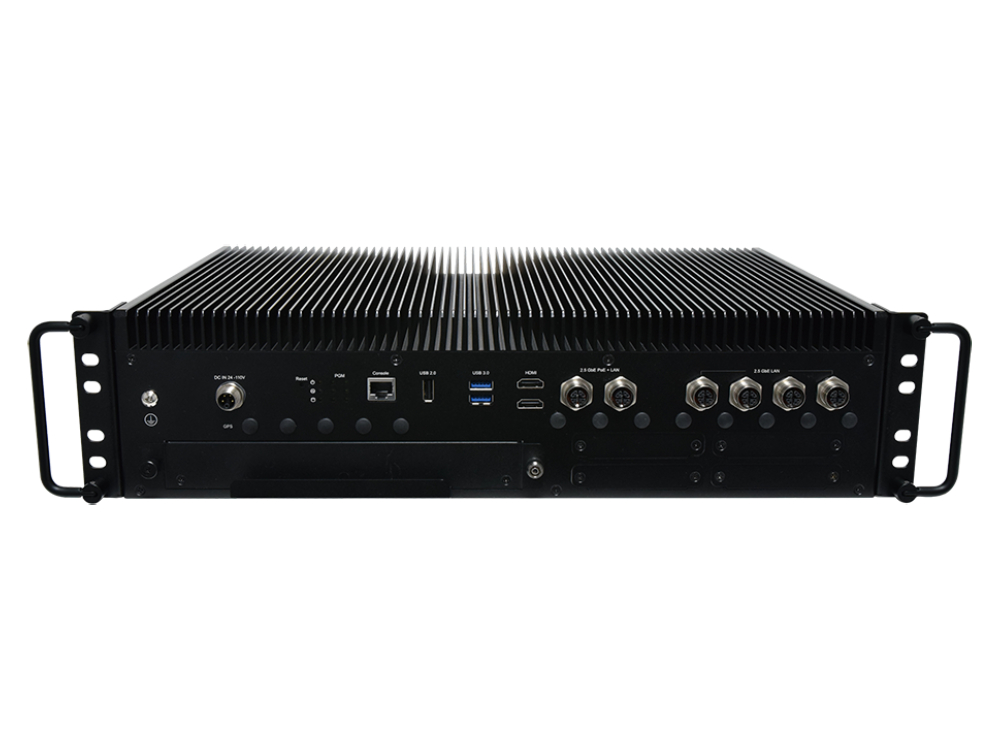
Lanner specializes in providing OT Security and Edge AI appliances fortified with Out-of-Band (OOB) functions. These OOB functions serve as a robust layer of protection, ensuring the integrity and security of operational systems against potential threats