In the dynamic world of network technology, ensuring uninterrupted and secure data transmission is more important than ever. One solution that stands out is optical fiber bypass, engineered to bolster network resilience, enhance security, and improve overall efficiency.
What is Optical Fiber Bypass?
Optical fiber bypass is a technology used in network infrastructure, specifically for optical fiber communication networks, to improve redundancy and reliability, protecting the network against multiple points of failure. This means if a certain part of the network fails, it will not affect the function of the remaining network. It's designed to ensure continuous and uninterrupted network service, particularly in scenarios of hardware failure or maintenance.
Why is Optical Fiber Bypass Important?
Optical fiber bypass, a technology utilized in network infrastructure, particularly enhances redundancy and reliability in optical fiber communication networks. By protecting against multiple points of failure, it ensures that if a segment of the network fails, the functionality of the remaining network remains unaffected. This design is aimed at providing continuous and uninterrupted network service, especially during hardware failures or maintenance periods.
Optical fiber bypass is frequently employed in environments such as data centers and by Internet Service Providers (ISPs), where the need for high-speed data transfer and dependable network performance is paramount. This technology is equally vital in large-scale enterprise networks that depend on optical fiber for rapid and efficient data transmission over extended distances. Furthermore, Optical fiber bypass contributes significantly to network resilience, acting as a fail-safe against physical damage, system failures, or disruptions due to maintenance, thereby bolstering the network's overall robustness and reliability.
Difference Between Optical Fiber Bypass and LAN Bypass
Optical fiber bypass and LAN bypass are designed for different network needs. Optical fiber bypass is ideal for large-scale, high-speed networks using optical fibers, perfect for long-distance, high-bandwidth transmission. In contrast, LAN bypass suits smaller, Ethernet-based LANs, focusing on local connectivity using physical or electronic relays. Recognizing these distinctions is crucial for effective network infrastructure design and management, catering to specific operational requirements.
Benefits of Optical Fiber Bypass
The implementation of optical fiber bypass offers several significant benefits. It notably minimizes downtime by maintaining network connectivity in situations of hardware failure or during maintenance activities. This technology also enhances scalability and flexibility, allowing network designs to be easily modified to meet evolving requirements without necessitating a complete overhaul. In terms of security, optical fiber bypass contributes positively by enabling the isolation of specific network segments during security breaches or maintenance, ensuring uninterrupted operation of the remaining network. Furthermore, by optimizing network efficiency and reducing downtime, optical fiber bypass can result in considerable long-term cost savings.
Multi-Mode vs Single-Mode Fiber Bypass
Multi-mode and Single-mode Fiber Bypass are two optical fiber configurations used for ensuring network reliability, differing in fiber type and applications. Multi-mode fibers, characterized by their larger core size, allow the transmission of multiple light modes, making them suitable for high-bandwidth, short-distance applications. Conversely, single-mode fibers, with their smaller core, are designed for single light mode transmission and cater to longer distances with higher bandwidth capabilities. While multi-mode fiber is commonly employed in local, short-haul applications due to its cost-effectiveness, single-mode fiber is the preferred choice for long-distance, high-capacity data transmission.
Conclusion
By creating alternate pathways for data transmission, Optical fiber bypass ensures that a failure in one part of the network does not disrupt the overall network functionality. This technology is especially critical in maintaining continuous and uninterrupted network service, proving invaluable in scenarios involving hardware failures or routine maintenance.
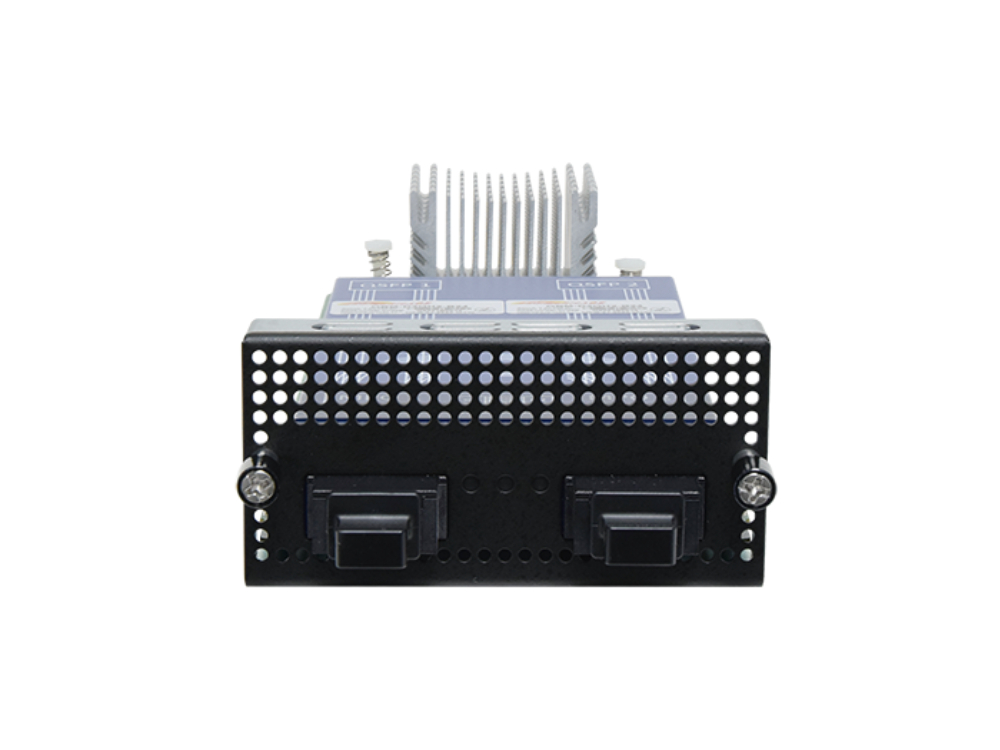
Lanner's NIC Module NCS2-IQM203, equipped with Intel® XL710-BM2 Ethernet controllers and 2x 40G QSFP+ ports, supports both multi-mode and single-mode fiber bypass. This module is an ideal choice for enterprise IT, cloud, and communication networks, offering broad interoperability, optimized performance, and enhanced flexibility, especially in virtualized environments and services.
Featured Product
NCS2-IQM203
NIC Module With Intel® XL710-BM2 Ethernet Controller And 2x 40G QSFP+ Ports
| CPU | N/A |
| Chipset | Intel® XL710-BM2 |
Read more