As entire global markets remain under the significant impact of the novel COVID-19 pandemic, 5G networks and services seem constrained due to the slowed down 5G devices sales, delays to spectrum auctions, and operators’ hesitance about investing in 5G infrastructure. However, though temporarily slowing down the 5G development, the reshaping of connectivity demands may be accelerating consumers’ willingness to embrace 5G. Just in the past few months, 5G has well demonstrated how it can help frontline healthcare service workers combat the diseases through remote-controlled devices or immersive technologies. Moreover, the heavy work-from-home traffic also led the consumers to realize how critical resilient connectivity is during a crisis like COVID-19 and in the future.
How does 5G turn the predicament into possibilities in mobile networking? It has changed the network design principles by:
- Isolating network capabilities and enabling the multiplexing of independent logical networks on the same physical network infrastructure with network slicing
- Creating differentiated services for individual application needs, e.g., high-bandwidth slices for high throughput applications, low-latency slices for mission-critical applications, and low battery slices for massive machine-type communications
- Allowing application content to be located at the network edge (where the data is produced –by IoT devices, local edge servers, or personal mobile devices)
To realize service virtualization and find a solution to address the emerging 5G/IoT requirements, a more advanced automation routing approach is essential, which should provide the most up-to-date view of network resources, intelligent algorithms, and smart network control methods. Instead of a technological revolution by starting from scratch, many carriers consider the gradual transition from 3G/4G to 5G a well-accepted evolution path for simplifying IP/MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) networks—Segment Routing.
Segment Routing (SR) is an IP routing protocol that simplifies the data packet forwarding/traffic engineering process on a network. It allows routers to carry routing information (a list of sequentially arranged segments/nodes as stops) in the IP packets to determine their forwarding path across the network. By way of analogy, we might think of SR as an automated luggage carrier; by attaching a unique tag with the list of stops from the departure to the final destination, the service forwards the luggage to each stop according to the sequence defined by the plan: Taipei→Tokyo→New York. In this way, the forwarding path is fully controlled, scalable, and simple. In other words, SR can not only solve MPLS’s complex issues and make up for its lack of scalability but takes MPLS one step further.
There is still a final push for SR to achieve successful implementation – out-and-out accurate network inventory and data. If the data accuracy is not guaranteed, the stringent service path requirements of 5G network slices will not be met in terms of low latency, resiliency for reducing risks, and bandwidth control.
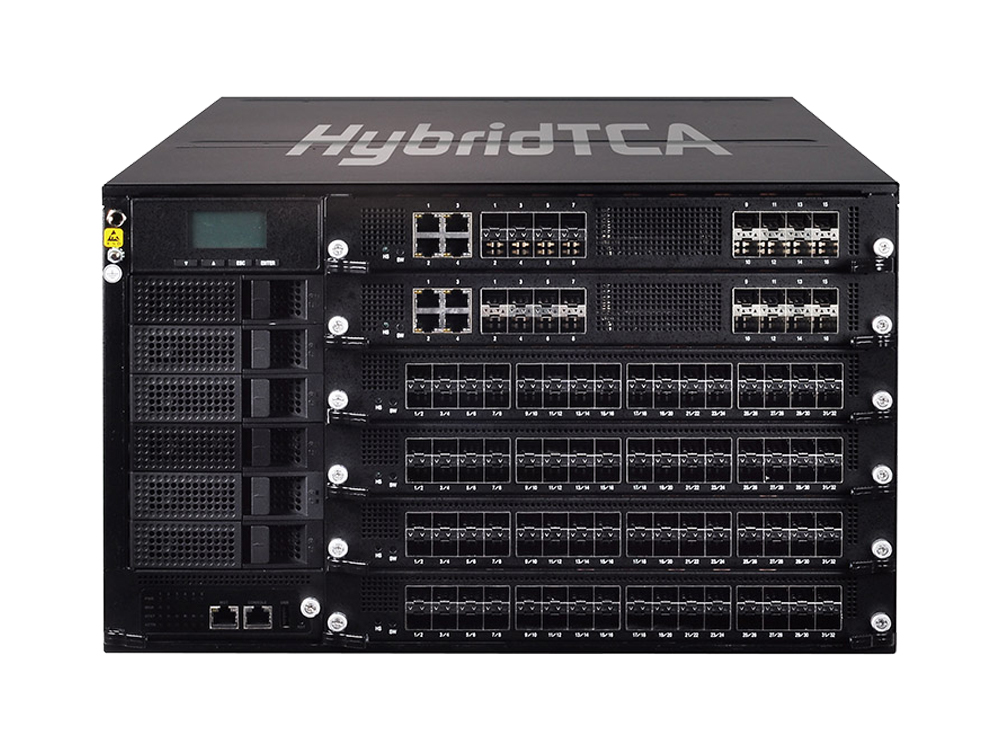
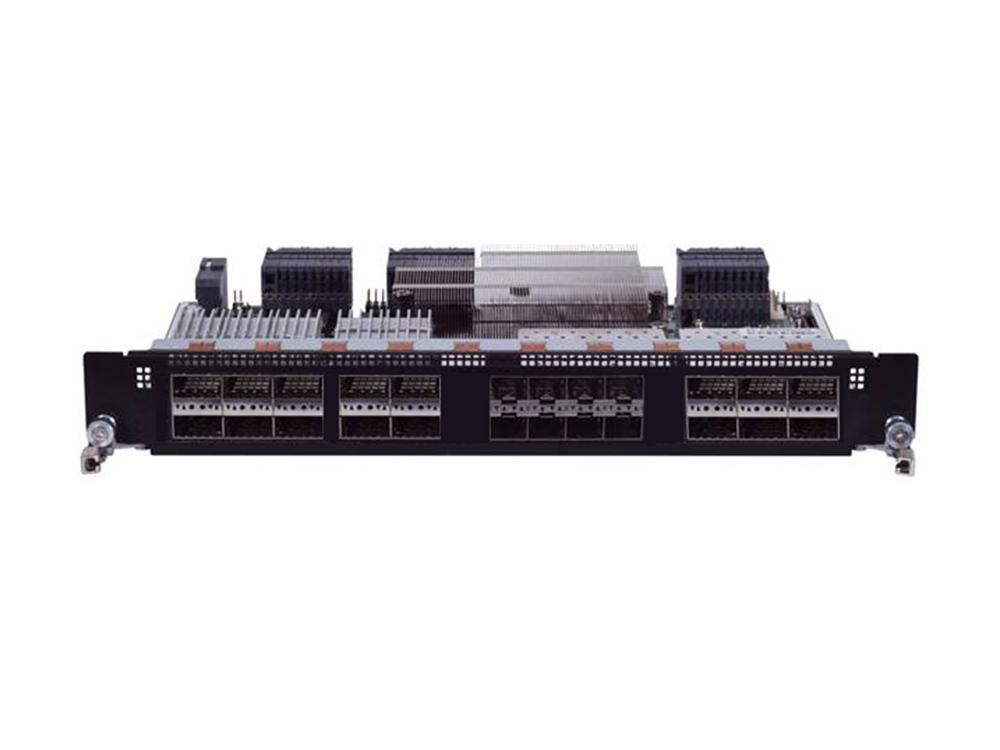
With Lanner/NoviFlow’s programmable forwarding plane solution that integrates network functions into one simple and deployable management, the existing packet forwarding and load balancing services are enhanced with SRv6 support, effectively reducing the overall cost that service providers have been bearing. Additionally, the deployment of Intel’s Tofino programmable switch fabric empowered by NoviFlow’s NoviWare Network Operating System both introduces a new variant of SRv6 binding segment for data forwarding service policy and provides path orchestration for it. Overall, Lanner’s solution delivers high throughput and dynamic/scalable network services, efficiently addressing large-scale deployments with cost-effective, dynamic scaling for highly variable demands.