Private 5G networks are emerging as the connectivity technology of choice for enterprises seeking to implement the transformative applications that drive smart factories, power plants, and the internet of things (IoT). A private 5G network gives companies the ability to customize the network according to specific organizational needs and locations, securely, and on their timetable.
Private 5G Potential & Benefits
A private 5G utilizes a smaller, more focused deployment to meet the specific availability, reliability, and service needs of the organization, with the potential to dramatically improve security, bandwidth, and speed. By delivering ultra-reliable, low-latency communications (URLLC), private networks can support advanced IoT, Industry 4.0, and mission-critical public safety applications.
Organizations that require high security, unique service offerings, and accelerated 5G deployment stand to benefit most from private 5G networks. Private 5G networks in smart factories can minimize wired connections, streamline data collection and analysis, and improve workforce safety. The manufacturing sector recognizes the low-latency, high-bandwidth communication of private 5G networks for material handling, robotics, and predictive maintenance innovations. Healthcare, education, and public transportation sectors are potential beneficiaries of private 5G deployments to enhance coverage, logistics, and security.
Private 5G Application Scenarios
The reduced latency and increased reliability make private 5G especially useful for industrial applications, such as manufacturing, and automotive, but it does not stop there, additional private applications include stadiums, malls, oil and gas refineries, and smart transportation systems.
Stadiums and shopping centers are large venues that demand high connectivity, for streaming content, augmented reality, and other high-bandwidth applications, during peak hours of operation, which through using a private 5G network can quickly streamline usage capacity, facility operations, and service delivery.
Oil and gas refinery sites are comprised of large geographic areas and include many critical machines, safety features, and sensors, and a private 5G network would allow the interconnected networks to be securely monitored and maintained in real-time.
Private 5G Requirements
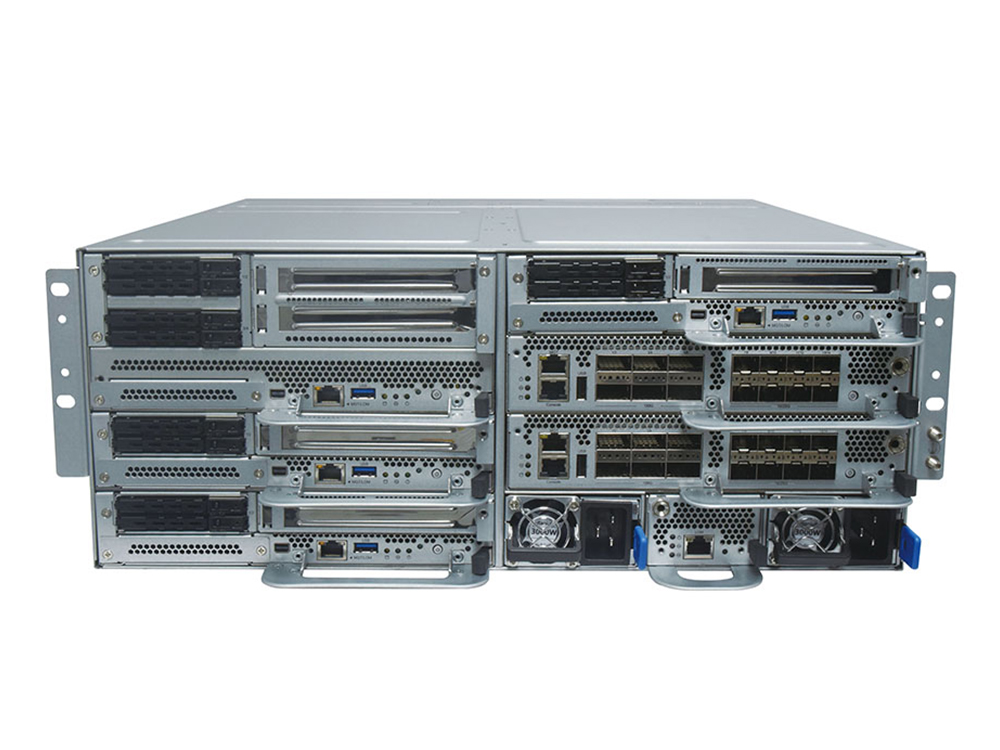
Requirements for private 5G network availability, reliability, application interworking, and even quality of service (QoS) can be more stringent than commercial network standard architecture. Private 5G networks require the implementation of a service-based core network architecture (SBA), in addition to beam-centric architecture with static and dynamic beamforming, to allow for more focus on performance, optimization, and location intelligence. Private 5G networks also require virtual software-defined networks (SDNs) to support network slicing and automated service delivery for enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low latency communications (URLLC), and massive machine-type communications (mMTC).
Private 5G & O-RAN
A private 5G network is an enterprise-dedicated network that is built using 3GPP standards, allowing enterprises to define and build their own wireless networks. This is also a chance for enterprises to move from proprietary legacy RAN to Open RAN (O-RAN) architecture. Open RAN has a mix-and-match architecture that can combine best-in-class RAN elements from multiple private 5G vendors. Operators benefit from the inherent competition and innovation introduced by O-RAN.
Private 5G Network: Small Cell Technology
Private 5G solutions can scale performance for indoor and outdoor wireless grid deployments through small cell technology, which utilizes smaller, short-range, distribution nodes. Small cell hardware can reduce complexity while meeting capacity demands for a high number of users over a large coverage area. Small cell transceivers can be easily mounted to walls, poles, and other common objects, with flexible backhaul options such as fiber, cable, and microwave.
Private 5G networks built with small cell mmWave nodes can utilize unlicensed frequency bands between 57 and 71GHz, which will allow less refraction and signal interference, especially in metal-dense buildings.
The Lifecycle of Private 5G Networks
- Development
Begins by determining the objectives, defining a high-level design, and developing all the elements required for this private 5G network solution. Organizations can build, design and operate their custom-made unique 5G network by working with telcos, private 5G network providers, and network testing experts.
- Deployment
The second stage is deployment, adapting the solution to the specific scenario of the particular site, and configuring, integrating, deploying, and testing the network. Private 5G deployment provides multiple options such as privacy level, QoS, multi-site coverage, spectrum utilization, and RAN customization.
- Operation & Maintenance
The main focus is the operation, maintenance, and network hardware and software updates. To optimize the network through daily management and design improvements.